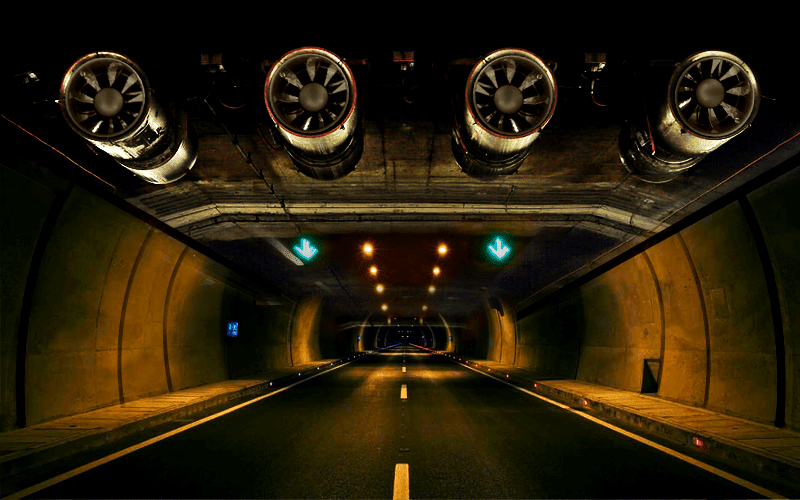

Smoke Ventilation in Tunnels
Fire safety engineering analysis can be conducted to demonstrate that the level of safety provided by a natural smoke ventilation system for the tunnels is equal or higher than a mechanical emergency tunnel smoke ventilation system in terms of tenability limits for evacuation as stipulated in NFPA502 and the fire safety requirements by the Authority Having Jurisdiction.
In general, there are 3 types of Emergency Smoke Ventilation Systems commonly used for Tunnels:
- Natural Smoke Ventilation Concept
- Longitudinal Mechanical Smoke Ventilation Concept
- Localised Mechanical Smoke Extraction Concept
Natural Smoke Ventilation Concept
Fire safety engineering analysis conducted to demonstrate that the natural smoke ventilation system is effective to maintain tenable conditions for evacuation as stipulated in NFPA502.
Natural smoke ventilation concept developed using CFD modelling and evacuation simulation based on the strategic natural louvre openings and the exit/entry points of tunnel to facilitate the smoke exhaust.
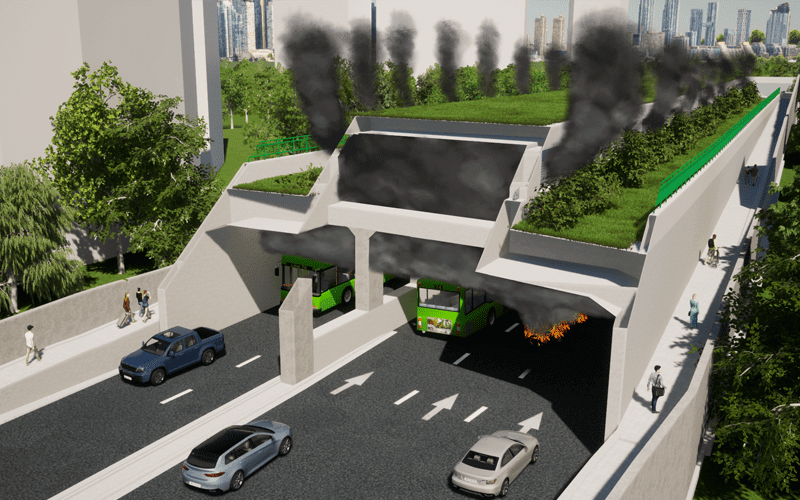
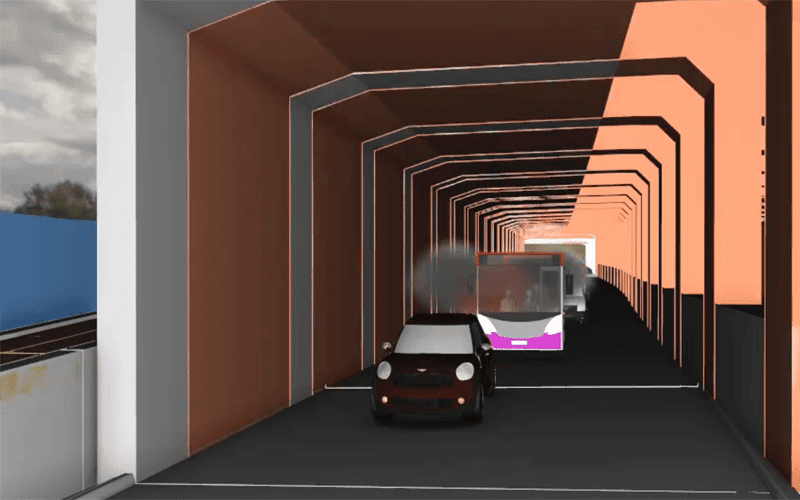


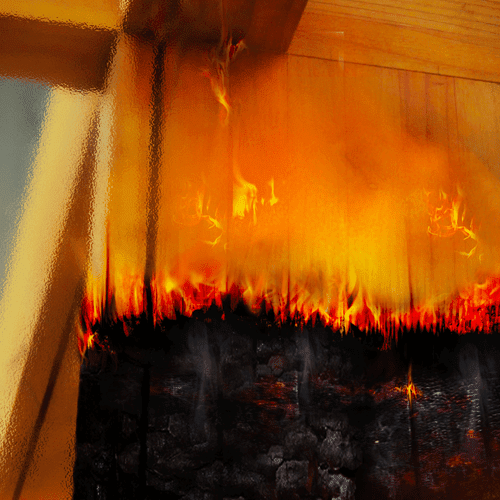
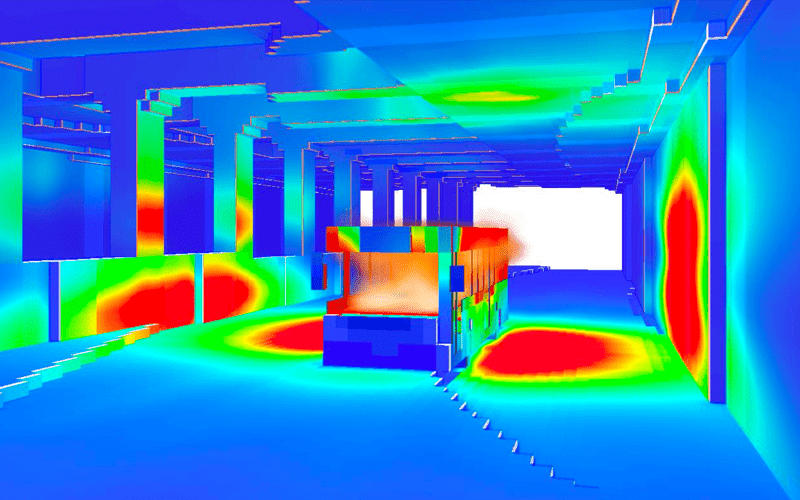
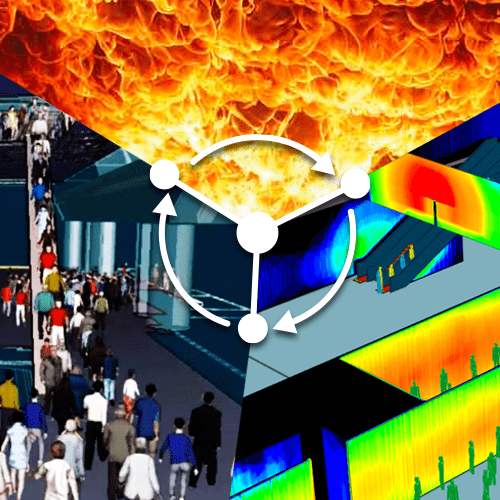
Fire and Smoke Modelling Simulation to assess Tenability Limits
Hot buoyant smoke and gases are released from the tunnel along the natural openings at the fire location to maintain a tenable smoke clear height of at least 2.5m above floor level for the safe evacuation of occupants.
ASET/RSET > 2 is achieved with at an acceptable level of life safety.
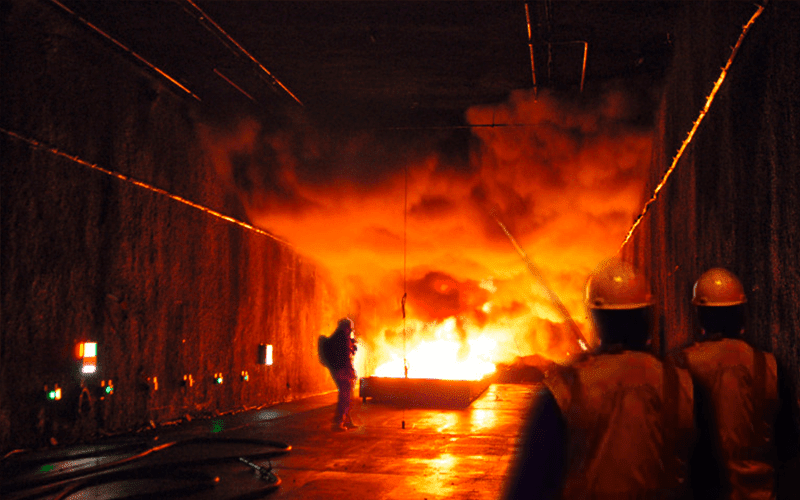
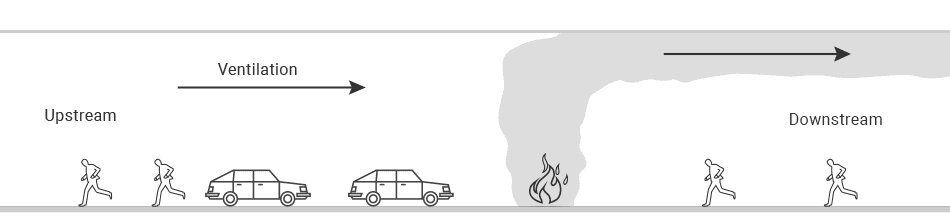
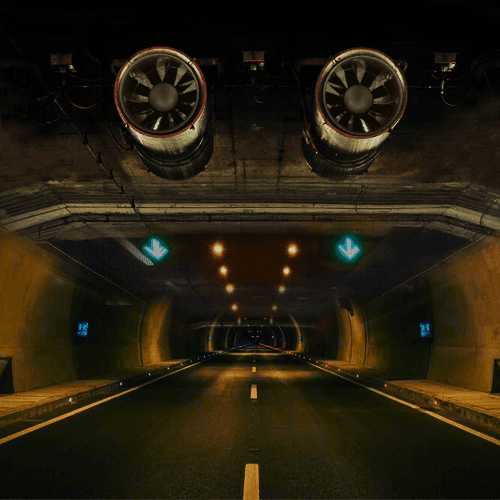
Longitudinal Mechanical Smoke Ventilation Concept
- Smoke is directed downstream along the tunnel in the opposite direction of occupant evacuation.
- Use of jet fans along the tunnel to establish the critical velocity concept.
- Applicable to uni-directional tunnel of length < 240m.
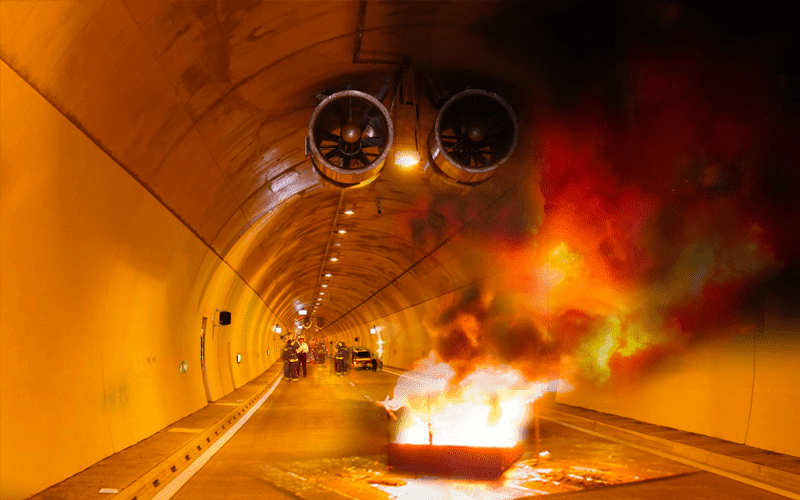


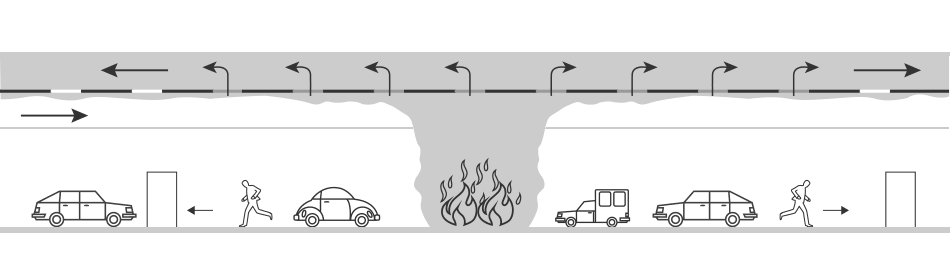
Localised Mechanical Smoke Extraction Concept
Smoke is extracted in the vicinity of the fire source to maintain tenable conditions along the tunnel for safe occupant evacuation.
- Smoke is extracted in the vicinity of the fire source to maintain tenable conditions along the tunnel for safe occupant evacuation.
- Use of smoke extraction ducts for localized smoke extraction at the fire location.
- Applicable to bi-directional or uni-directional tunnels.
Fire Detection Systems for the mitigation of tunnel fires
Smaller design fire sizes can be mitigated with tunnel fire detection and warning systems to activate the fire suppression systems.
Commonly used fire detection systems;
- Video Image Detection (VID) System (video flame and smoke detection)
- Video Infra-Red System
- Spot or Linear Heat Detector with temperature sensors.
















Contact Us
Follow us on: